|
HMC DOCKYARD HALIFAX
History of HMC Dockyard Halifax - from the website of the Halifax Military Heritage Preservation Society
Halifax was established by the British in 1749 to expand their presence in Acadia – today‘s mainland Nova Scotia – and to counter the fortress at Louisburg on Île Royale (Cape Breton Island) that France had built earlier that century. The Royal Navy (RN) began to use the major harbour at Halifax as a fleet anchorage for operations in the region soon thereafter, with the French and Indian War beginning in 1754, leading to the broader Seven Years War in 1756.
In 1757 Vice-Admiral Francis Holburne‘s fleet blockading Louisburg suffered considerable damage from a hurricane. With the nearest naval repair facilities in distant England, Jamaica and Antigua, the Admiralty decided, as a result, to create such a facility in Halifax. The first attempt was to create a careening wharf on Georges Island in Halifax Harbour, but the work being undertaken in that exposed location was promptly destroyed by a northerly gale. The next location chosen, at Gorham‘s Point, was a mile north of the Halifax town walls, where HMC Dockyard now stands. To the initial two-acre site, seven additional acres were added the following year. Construction began in 1758 and the first careening wharf was in place by the summer of 1759, understood to have been supervised by Sailing Master James Cook – later Captain and famed Pacific navigator and explorer. The new naval yard – the King‘s Yard – was formally established by an Order-in-Council on 7 February 1759 and was the first royal dockyard in North America. It would be a strategically significant base for the Royal Navy for the next century-and-a-half, until Britain‘s withdrawal from Canada in 1906.
The naval yard initially consisted of a capstan house to accompany the careening wharf, a mast house and associated mast and spar ponds, a boathouse and storehouses. A sail loft was added in 1769 and a dockyard clock was installed on its peak in 1772. The same clock, presented to the City of Halifax by the Royal Canadian Navy in 1996, is the only remaining feature from the 18th century naval yard and the oldest working timepiece in Canada, predating the Halifax Town Clock on Citadel Hill by 31 years; it stands today outside the Halifax Ferry Terminal at Chebucto Landing.
Repairs and upgrades to the King‘s Yard were conducted in a piecemeal fashion whenever Britain found itself in a conflict. The period between 1775 and 1818 saw significant development of the yard as Britain was engaged in the American Revolutionary War, the French Revolutionary War, the Napoleonic Wars and their North American sideshow, the War of 1812. Defensive blockhouses were added on the landward side of the yard and Forts Coote (1775), Needham (1778) and Duncan (1793) were established for greater protection, and a house for the Resident Commissioner was built in 1785. Additional land was acquired to the north of the naval yard in 1783 and a naval hospital and victualling yard were established, which included also a dead house (morgue), “lunatic cells,” a fever (quarantine) ward, wharf and ancillary buildings. A second mast pond was created in 1784 in the northern part of the yard. A large, triple residence was constructed in the victualling yard in 1815 which is still used today as senior officers‘ residences - the oldest remaining dockyard structure. The hospital burned in 1819 and a replacement with its own jetty was finally built in 1863, becoming the Royal Naval College of Canada in 1910 after the British departed. A magazine was added north of the hospital in 1872.
When Britain transferred the naval yard to Canada in 1905 the facilities consisted of 24 acres of land, the hospital, victualling stores, coal stores, various workshops and residences (some 75 buildings), five wharves and three slipways. The yard remained largely dormant until the start of the First World War in 1914, when it again was upgraded for use. Wharves were added along with additional storehouses and workshops – in total 12 new site features were introduced.
The Halifax Explosion on 6 December 1917 caused extensive damage to the dockyard. The Royal Naval College of Canada was nearly ruined and several cadets and staff injured, two other buildings were destroyed and virtually every other building was damaged. Naval casualties from the blast were 22 killed and 8 injured.
Limited maintenance and modernization was done at the dockyard in the inter-war years and many buildings were removed. By 1938 only six of the 75 buildings transferred from Britain to Canada in 1906 remained. The Second World War (1939-45) would see the last 19th century dockyard buildings torn down as well as all pre-1935 buildings in the southern part of the yard, to be replaced with modern facilities during the dockyard‘s greatest period of change. The capstan house and sail loft, which had existed since 1759 and 1769 respectively, were torn down in 1940. Over the war years 67 new site features were introduced, 14 of which were still part of the dockyard in 1995.
Since the Second World War a number of new buildings have been added, the most prominent of which are Fleet Maintenance Facility Cape Scott (named the Prince of Wales building) in 1983, the Maritime Forces Atlantic Headquarters (1984) and the Main Base Supply Building (1996). The synchrolift for lifting submarines out of the water was built in 1968 after the RCN acquired three Oberon-class submarines, and the associated submarine shelter was added two years later.
Today‘s HMC Dockyard is completely unrecognizable from the King‘s Yard of the 18th century. The site of the original capstan house and careening wharf was about where the Main Base Supply Building is located with the logo “Canada‘s Atlantic Fleet,” that can be seen from Barrington Street just south of the Macdonald Bridge. A large scale diorama depicting the naval yard as it existed in 1813 is displayed at the Maritime Museum of the Atlantic in Halifax.
The dockyard is today the home of the Royal Canadian Navy‘s Atlantic Fleet, consisting of seven Halifax-class frigates, six Kingston-class coastal defence vessels, one or two Victoria-class submarines and, currently under construction (2020), four Harry DeWolf-class Arctic and offshore patrol ships. The dockyard additionally hosts visits by warships from Canada‘s allies, such as the United Kingdom, the United States and various other NATO and friendly nations, and provides a winter berth for the iconic Second World War corvette HMCS Sackville, Canada‘s Naval Memorial. HMC Dockyard forms part of Canadian Forces Base (CFB) Halifax, the largest Canadian Forces Base in Canada with approximately 10,700 military and civilian personnel.
HMC Dockyard was designated a National Historic Site of Canada in 1923.
HMC Dockyard Halifax - Employee's Guide Book 1946 (reprint from 2009)
"H.M. Naval Yard Halifax, NS, HMS Pyramus" Date: circa 1870
The Pyramus was an old teak Danish-built, first-class 28-gun frigate, that was captured with seven others by Nelson at the Battle of Copenhagen. The eight vessels were quite new at the time and lay on the stocks. They were launched by Nelson, fitted with jury masts and sent to England. The Pyramus was sent about 1833 or earlier to Halifax, Nova Scotia, where she is shown moored alongside one of the Naval Yard wharves, offering a strange contrast to the modern specimens of shipbuilding of the day. The hulk was used as a hospital for invalid men-of-war, and also as temporary accommodation of the crews of vessels refitted in the dockyards. During the outbreak of cholera in Halifax, this boat was taken from the Dockyard to quarantine and used as a hospital ship. She was later brought back to the Dockyard and sold to Mr. Saul Mosher, who demolished the vessel about 1887.
Source: Nova Scotia Archives Photographer: Notman Studio Reference: Notman Studio Nova Scotia Archives 1983-310 O/S no. 39065
Halifax Harbour c1890-1900 - This image was made from a broken glass negative
Written on the side of the photo "71101 1/2 Halifax from harbour"
Click on the above photo to see the full image Photo courtesy of Gary Wilson
Steam Tug A.O. Whitney in the left foreground. The A.O. Whitney was built in Boston in 1873. The schooner astern of her is the Nicanor, built in 1889 in Mahone Bay, NS. On the right of the photo is Saint Patrick's Church with Saint George's Round Church to the left of it.
Click here to see the image with the line from the broken glass edited out
Click here to read an article from 1899 that mentions the tug A.O. Whitney
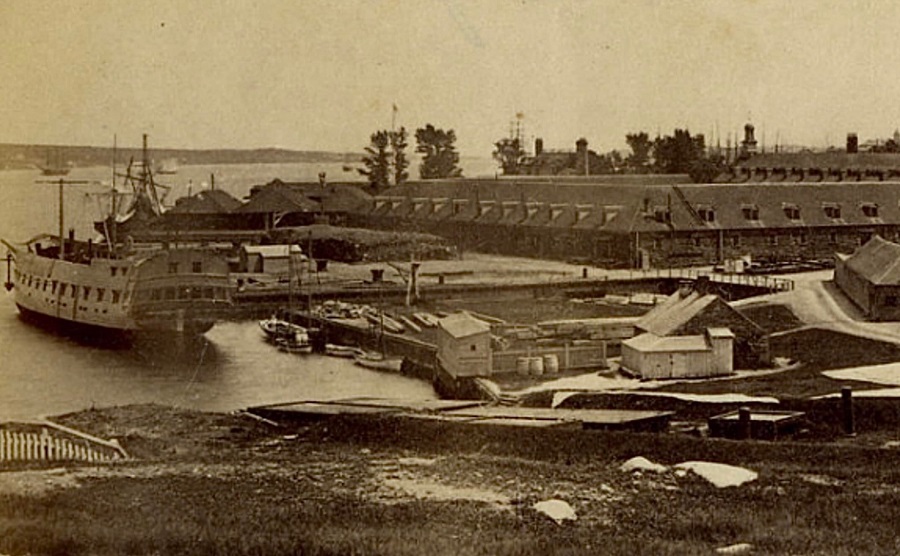
(NMoH-Dkyd-001) Halifax Shipyard (NMoH-Dkyd-002) HM Naval Yard c1860s (NMoH-Dkyd-003) HM Dockyard 1867. HMS PYRAMUS on left of photo. See write-up for the NS Archives at the top of the photo section. (NMoH-Dkyd-004) HM Dockyard c1870s (NMoH-Dkyd-005) Halifax Harbour and Naval Yard - undated
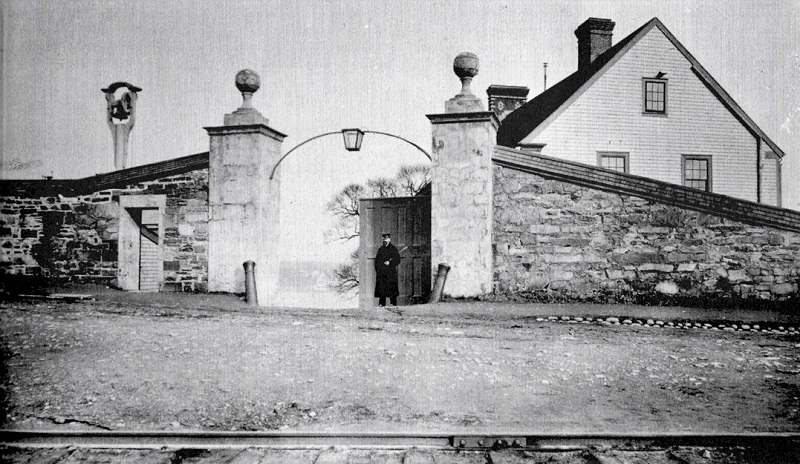
(NMoH-Dkyd-006) HMC Dockyard Main Entrance c1890 (NMoH-Dkyd-007) HMC Dockyard South Gate - Jun 1926 // RCN Neg # HS 05736 (NMoH-Dkyd-008) RCN personnel playing hockey on a ring in HMC Dockyard, Halifax. The back of the photo reads "residence number seven, 1943-44, parade square" Courtesy of the Naval Museum of Halifax
Various warships alongside at HMC DOCKYARD Halifax
(FM621) HMCS WENTWORTH K331 and HMCS MATAPEDIA K112 alongside in Halifax (FM622) Destroyers and Corvettes in Halifax - 1942 (FM623) HMCS MEDICINE HAT J256, unknown corvette and HMCS GROU K518 in Halifax (FM624) Unknown Frigate and Corvette alongside (FM625) Frigates at Jetty 3 in Halifax. HMCS SAINT JOHN K456 outboard
(FM626) HMS MONTGOMERY G95 centre ship (FM627) Fairmile MLs 109, 107 and 095 with unknown ship inboard, Halifax (FM628) Unknown ships alongside in Halifax (FM629) HMCS HAIDA G63 inboard destroyer, outboard destroyer unknown (FM630) HMCS DUNDALK Z40 outboard of the frigate HMCS STRATHADAM K683, Jetty 3, Halifax - 1944
From the collection of François Messier, AB, RCNVR
Courtesy of Denis Messier
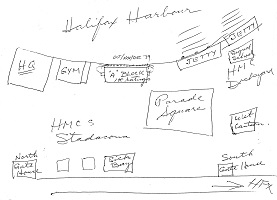
(LK27) Sketch of HMC Dockyard 1939 Sketch drawn by Lionel Kennedy c1983 From the collection of LCdr Lionel Kennedy, RCN Courtesy of Barbara Holliday
Buildings in HMC Dockyard Halifax c1941/42 From the collection of Ross Somerville, Leading Coder, RCNVR
Various ships in HMC DOCKYARD - Apr 1970
(RA01) HMCS ST LAURENT, Jetty 2, next to synchrolift - Apr 1970 (RA02) HMCS CAPE SCOTT - Apr 1970 (RS03-RS04) Four ships nested at Jetty 3 - inboard to outboard: HMCS OTTAWA, ASSINBOINE, ANNAPOLIS, TERRA NOVA - Apr 1970
(RA05) HMCS Ojibwa SS72 (inboard), HMCS Onondaga SS73 (middle), outboard sub unknown at Jetty 5 - HMCS BONAVENTURE in the background at Jetty 4 - Apr 1970 (RA06) HMCS BONAVENTURE at Jetty 4, bow south - Apr 1970 Courtesy of Richard Larcheveque
(DkydH001) HMCS PRINCE HENRY port side to in HMC Dockyard, Halifax. HMCS COLUMBIA I49 and HMCS ANNAPOLIS I04 on her starboard side (DkydH002-DkydH003) Ships lit up for Christmas in HMC Dockyard, Halifax - Dec 1958 (DkydH004) HMC Dockyard postcard. Jetty 3 in the foreground. Photo taken from the Angus L. MacDonald bridge, Halifax. Foreground outboard ship - HMCS ANNAPOLIS 265 (DkydH005) HMC Dockyard. Jetty 3 in the foreground. Photo taken from Angus L. Macdonald bridge, Halifax. Foreground outboard ship - HMCS CRESCENT 226 // Courtesy of Claude Mathes
(DkydH006) HMCS HURON 281 in refit, inboard of HMCS ST CROIX 256 at Jetty 3 - summer 1979 (DkydH007) HMCS WILLIAM HALL at Jetty 3 in HMC Dockyard, Halifax - 26 Feb 2023 // Photographer: Kevin Whittle // Courtesy of Kevin Whittle. © 2024 // Note the changes to the dockyard from the 1979 photo to this photo in 2024. (DkydH008) HMCS SAGUENAY, NIPIGON and TERRA NOVA in HMC Dockyard, Halifax. Photos taken from the McDonald Bridge // Courtesy of David Ross
Jetty "NJ", HMC Dockyard Halifax with 2 AOPS alongside - 2023 Source: Apple Maps Satellite Image
|